NMN - Nicotinamide Mononucleotide safety and risk management
NAD boosters are a hot topic. NMN is the hottest 🔥
One of my favourite ways to analyse the latest health action in longevity technologies is to use Google’s keyword planner and trends tools. They form a great way to track the ‘pulse’ of human interest on healthspan. And as I planned my next upcoming series of blog posts on NAD boosting with NMN and diving deep into epigenetics and biological age, I certainly found plenty of evidence of our collective curiosity on the topic.
Given the introduction of nicotinamide riboside (NR) and more recently nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) as supplements over the past four years, many in the longevity community are self-experimenting with these molecules. And while the requisite clinical trials (those in humans which reveal their effectiveness) are still ongoing, it is clear from the data and trends I analysed that these molecules, particularly NMN, are moving into the mainstream. Heck, I’ve even run into many folks in the energy sector (where I run my day job - Solcast), taking NR and/or NMN!
Trends in NMN and NR over time
Here is a great illustration on how the search analysis for NR and NMN have changed over time. While NR got an early boost with the launch of Elysium Health and their product “Basis”, searches quickly returned to baseline within a matter of weeks.
NMN however, after an outstanding boost from David Sinclair’s appearance on the Joe Rogan Experience podcast, and likely supported by Dr. Sinclair’s impressively wide-reaching Lifespan book launch tour, has clearly achieved a wider and more sustained appeal. NMN is clearly the hottest topic in the world of NAD+ boosters, and this is supported further by the search results present in many English speaking countries, with thousands of searches for NMN and related topics each month (and growing steadily).
What is NMN? What are the benefits?
It is hardly my role to explain the basics of NMN and NAD+ boosting supplementation, as that is not the focus of the A Longer Life (here we focus on decision making, actionable insights). Thankfully however, my mate from across the pond Dr Brad Stanfield (New Zealand) runs a fantastic and educational YouTube channel covering these topics. You should be able to find the resources you need to become more familiar with NAD+ boosting supplementation by watching his videos (be sure to SMASH that like button 😂).
NMN supplementation: Safety, strategy, sourcing
There are however three key questions that A Longer Life will engage with on the topic of NMN. These are:
Is NMN safe for self-experimentation?
How can we self-experiment to determine efficacy?
What NMN supplement should I use?
In this post, we’re looking into NMN safety and risk management. We’ll come back to #2 and #3 in future posts.
NMN supplementation: Is it safe? (Key question #1)
When exploring NMN supplementation safety, there are two important sub-questions to explore:
1) Has the molecule been found to be safe by reputable third-parties?
2) Are there known risks with supplementing the molecule?
NMN safety
Perhaps the most compelling safety certifications a molecule can receive is the GRAS accreditation from the FDA. GRAS - Generally Regarded As Safe status has been awarded to NR, as well as other forms of Vitamin B3 such as Niacin and Nicotinamide. NMN however has not yet reached this hurdle as of mid 2020.
However, in my opinion, this is inevitable, will arrive soon, and there are currently no reasons other than timing and resourcing as to why this has not yet occurred. NMN supplements are just entering the market en masse (see the above analysis!), and the FDA will be certain to react to this. To be clear, I am not asserting its safety independently, this is the role of the FDA. What I am saying is that closely related molecules have received GRAS status, and the lack of GRAS status for NMN is related to its relative newness in the world of supplementation not due to any known risks.
In summary, NMN is likely to become Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), and the other members of the Nicotinamide family (NR, Niacin) have GRAS status. We presently have no reasons to doubt it is a safe molecule to ingest.
NMN supplementation risks
However, GRAS status doesn’t ensure it will yield us a positive longevity based outcome. It more or less means it won’t poison us. Safety in this context does not mean there are not risks.
Nicotinamide. Source: Wikipedia
I have spent many tens of hours studying scientific publications available on the topic of Vitamin B3 supplementation and other closely related molecules to NMN (NR, Nicotinamide). What I have found clearly suggests supplementation of Vitamin B3 and its related molecules at high doses. At the most fundamental level, NAD booster supplementation of any form, results in adding significantly higher amounts of B vitamins into the body than it is prepared to metabolise. This is what I would refer to as ‘high doses’ in this context - specifically, consuming 1, 2 or even 3 orders of magnitude greater than the RDA for the vitamin group.
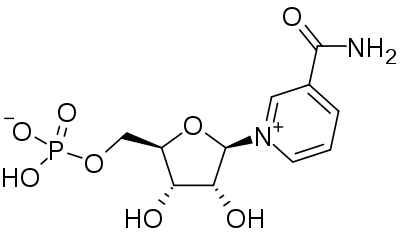
NMN! Source: Wikipedia
Conversely, my research also cemented the claims behind high dose supplementation, as there are a wide array of purported benefits for NMN (limited to mouse studies at the time of writing) and even greater supporting evidence for the benefits of NR (which NMN is converted into prior to entering cells) including early studies in humans. I won’t delve into all of these benefits - if you’re reading this post, you’re likely already sold on the benefits!
In making a judgment call, one is left with a risk management scenario. The possible benefits are significant. However, there are risks associated with high doses of B vitamin intake. To gauge how we make a decision, we turn to the fundamentals of risk management. Understand the motivations for the activity, diagnose the risks of the activity, apply a risk management strategy, and make a decision based on the residual risk.
This means, we next need to understand the risk better, after which we look at the options to managing the risk.
From the abstract:
“However, possible adverse effects and their mechanisms are poorly understood. High-level NAM (Nicotinamide) administration can exert negative effects through multiple routes. For example, NAM by itself inhibits poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), which protect genome integrity. Elevation of the NAD+ pool alters cellular energy metabolism. Meanwhile, high-level NAM alters cellular methyl metabolism and affects methylation of DNA and proteins, leading to changes in cellular transcriptome and proteome. Also, methyl metabolites of NAM, namely methylnicotinamide, are predicted to play roles in certain diseases and conditions.”
NMN supplementation primary risk - depletion of Methyl Pool
In my review, the primary risk of NMN supplementation (or NR), is the depletion of the methyl group ‘pool’ on which many aspects of your metabolism interact and modulating your DNA expression depend.
A recent study in the journal Biomolecules shares the work of South Korean duo Eun Seong Hwang & Seon Beom Song, who approach this topic from the same place that we opened this blog post - Vitamin B supplementation is growing dramatically in all forms, what are the possible consequences?
Of the many possible negative effects of NMN supplementation, only one of these has been determined to be highly probable. In fact, based on the fundamentals of organic chemistry, it is nearly certain to occur.
Taking high doses of Vitamin B3 (NAM, NMN or NR) will increase the demand on your available methyl pool. This means there are reduced methyl groups available for the methylation of DNA (which, for example, operates in the epigenetic expression of DNA via histones). This could have the deleterious effect of altering your patterns of gene expression and thereby impacting the supply of proteins your cells need to encode for important processes such as cellular repair or replication.
I have adapted the below image from the Biomolecules paper in order to add a bit of clarifying sign-posting on the diagram. From left to right, we have the flow of potential consequences of elevated NAM intake. At far left, the methylation cycle is represented, and at the nexus of it and the NAM cycle, we can see the methylation of NAM (to metNAM) occur. This is what will need to occur in high doses of Vitamin B (NR, NMN or any other form of NAM).
NMN supplementation risk management
Having understood the risk, analysis reveals a critical system (DNA expression, protein encoding) depends on the methyl groups which high doses of Vitamin B are likely to deplete.
So now the question is, can we employ a risk management strategy to minimise this risk?
I believe the answer is yes. Thankfully, it is possible to replenish the cellular methyl pool exogenously via supplementation. Allow me to explain a bit further.
At left in the above image, is an input to the methylation cycle via betaine. Betaine is a metabolite of choline (note how the methylation cycle flows from betaine to choline) and is one of the most important methyl ‘donors’ (another being folate). Betaine can also be called ‘Trimethylglycine’ (TMG). More broadly betaine actually refers to a class of molecules, but in the context of metabolism TMG and betaine are used interchangeably.
TMG is our risk management strategy when it comes to high dose NAM supplementation (including NR and NMN). This molecule is formed of an amino acid (glycine) that has three methyl groups attached to it. It is these three methyl groups that provide the extra inputs we need to support our ramped up methylation cycle when supplementing with NAM. It is possible that different forms of methyl groups, not provided by TMG, could also be required. This will be the subject of future research and updates to featured on the A Longer Life.
NMN and NR supplementation gets the green light
Based on the deep dive of research I have been completing on the topics of NAD+ boosters and epigenetics + biological age, I believe NMN supplementation to be risk-appropriate and a potentially effective tool in my longevity supplement stack.
I will soon be embarking upon my own NMN self-experimentation, and as I do so, I will be supplementing with Tri-methyl glycine (TMG) on a 1:1 basis with my NMN intake. In my view, the supplementation of TMG provides self-experimenters with an appropriate risk management strategy for long-term (i.e. more than 1-2 months) NMN (or NR) supplementation.
 |
Snag yourself some TMG!
FDA & TGA DISCLAIMER
This information is intended for educational purposes only and is not meant to substitute for medical care or to prescribe treatment for any specific health condition. These blog posts are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease, and only may become actionable through consultation with a medical professional.